|
Tracking Bandwidth - NetHogs
Posted by Will Kruss on 31 May 2016 02:37 PM
|
|
|
NetHogs is a utility which allows you to see what bandwidth each process on your system is using at a given time. * Please note this article contains extracts from: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-find-out-what-process-is-using-bandwidth/ Instead of breaking the traffic down per protocol or per subnet, like most such tools do, it groups bandwidth by process and does not rely on a special kernel module to be loaded. So if there's suddenly a lot of network traffic, you can fire up NetHogs and immediately see which PID is causing this, and if it's some kind of spinning process, kill it. Install nethogs under Debian or Ubuntu LinuxType the following apt-get command to install nethogs package: Install nethogs under RHEL or CentOS or Fedora LinuxFirst turn on EPEL repository and type the following yum command to install nethogs:
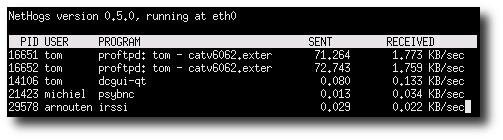
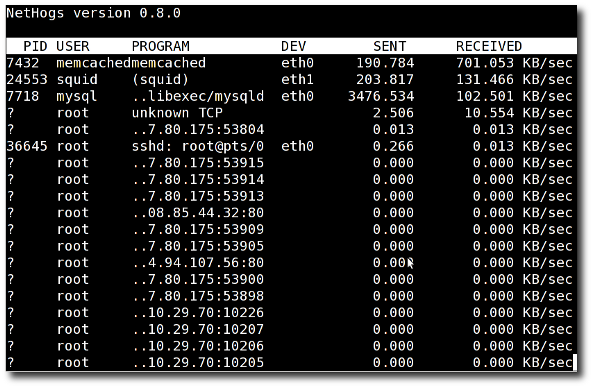
How do I use nethogs?The syntax is: nethogs nethogs eth1 nethogs [option] eth0 eth1 nethogs [option] eth0 eth1 ppp0 sudo /usr/sbin/nethogs eth0 Sample outputs:
Keyboard shortcutsUse the following interactive controls:
| |
|
|